Get 40 Hours Free Developer Trial
Test Our Developers for 40 Hours at No Cost - Start Your Free Trial →
Blockchain-based distributed ledger technology is preferred by businesses based on its speed, low cost, and high security. Open blockchains can be accessed by anyone and they are transparent. Creating a distributed network that allows individuals to see and control economic activities was the original intent of blockchain technology.
Blockchain needs an invitation from an organization that is eager to conduct business with a specific member, so it can build a growing network. Faster transactions are also among their main advantages.
Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains are faster since they only have a limited number of participants. Furthermore, private blockchains have lower storage costs.
In a time when more and more blockchain experts are focusing on speed and privacy concerns, many organizations are confused about choosing between the two.
The business’ decision will depend on its goals – is it looking for the openness a public blockchain provides?? Or is it more interested in privacy? Those looking for specific purposes rather than wide-ranging purposes and looking to exert control over transactions should choose the latter one. Decentralized peer-to-peer networks are being offered by blockchain application development companies and are based on a community or utility basis.
A public blockchain is perfect for organizations that want to gain customers’ trust through greater transparency. Private blockchains, however, are best for enterprises seeking privacy.
A pharmaceutical company, for instance, may find a blockchain app developed privately more beneficial. They travel from manufacturer to distributor through the supply chain.
Also Read, Search Engines Powered by BlockChains.
Blockchain vs DLTs
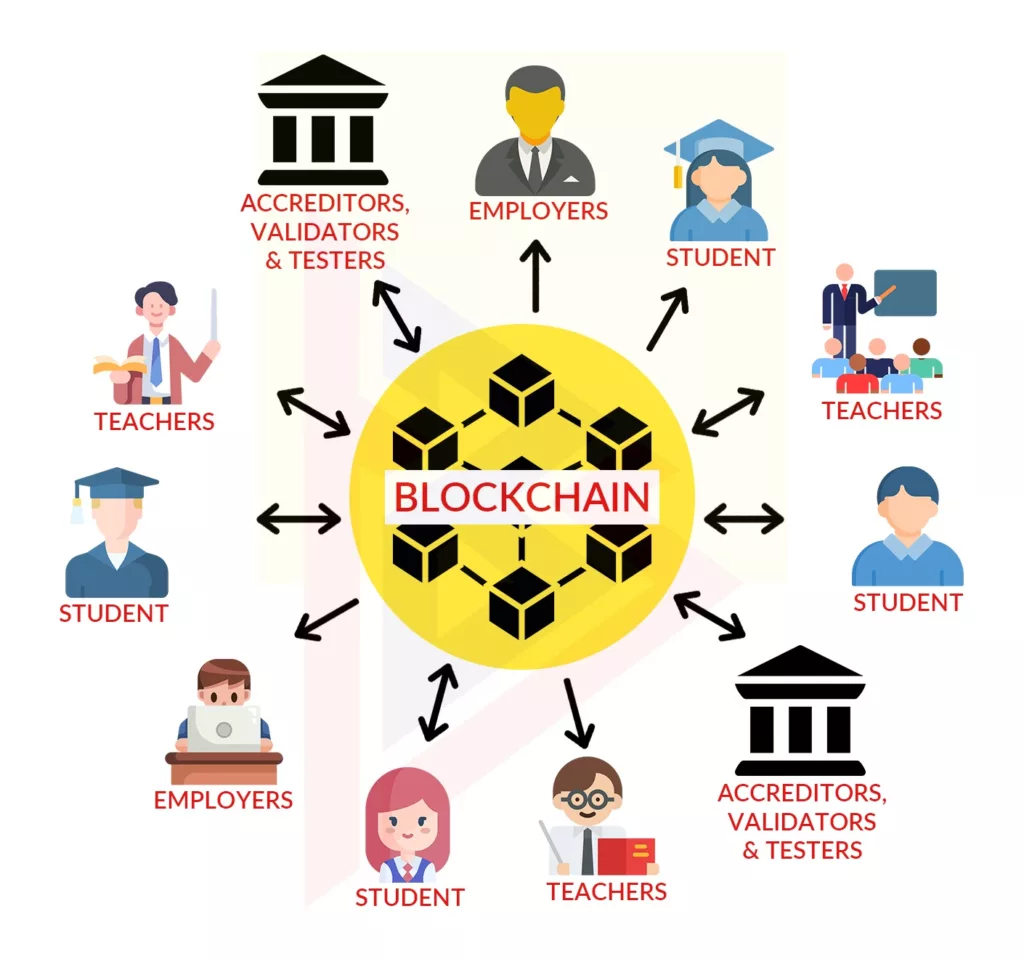
Before we dive into the details, we should clarify the confusion between blockchain and DLTs. Decentralized databases, also known as distributed ledgers (DLTs), are managed by multiple participants across multiple nodes. The umbrella, therefore, encompasses all decentralized database services that are governed and managed by participants.
A blockchain is in fact a type of distributed ledger technology. Blockchains and DLTs are both digital logbooks of records shared across networks of users. But that’s about all they have in common.
Fundamentally, blockchains are known for the creation of a string of timestamped data blocks that are periodically validated by the users on the network – meaning that new blocks can only be added with the consent of the other users.
The main difference between distributed ledgers is that not all DLTs deal with cryptographic validation before data is updated on the network. With some DLTs, the administrator has complete control over the network’s management, dictating the platform’s goals, structures, and functions.
As the popular Greek syllogism of logical argument suggests, not all DLTs are blockchains, but all blockchains are DLTs.
Read about the Python Trends here.

As we discussed, there are different types of blockchains. We can divide them into three categories:
- Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum
- A private blockchain like R3 Corda or Hyperledger
- A hybrid blockchain, such as Dragonchain
Public Blockchains:

In addition to being, known as permissionless blockchains, these platforms are open-source, decentralized networks that allow anyone to participate by becoming a user, a developer, a miner, or a member of the community. We are open and transparent in our operations, giving anyone access to and control over data at any given time.
Private Blockchains: Public blockchains are the opposite of permission blockchains, also called permission blockchains. Individuals with specific credentials/IDs are, allowed to access the network and use the data.
Hybrid Blockchains: Hybrid blockchains combine the best features of private and public blockchains, allowing for the security of sensitive data while enabling public validation of transactions.
A detailed explanation of Public Blockchains and Private Blockchains
Public Blockchain
Litecoin, Ethereum, and Bitcoin use the public blockchain model. This is a distributed ledger by design. Blockchain development services work in an open system where anyone can join the ledger, and any user present can also edit it.
The public blockchain is, not only decentralized but also fully distributed, as every node has the same power and transmission capacity. Each constituent node should approve the transaction through the consensus process in order for it to be valid. The record can then be, added to the chain once the authorization process is, complete.
Using this type of blockchain app development, peers are, encouraged to join the network as well as verify the transactions.
The Biggest Disadvantage of the Public Blockchain
Due to its complete openness, it is its greatest disadvantage. There is very little or no privacy offered by this type of transparency, and its security concept is weak. Additionally, the maintenance of the ledger requires substantial computing power. This type of network requires much work to achieve consensus due to its many nodes and transactions.
Read about the Best ASP.NET Tools To Build Mind-blowing Web Applications, here in our blog.
Private Blockchain
Private Blockchains, however, find their use in permissible networks; they are important for forks of the original blockchain. A private blockchain can only be, accessed with an invitation. The network starter then validates the access.
We will be, able to contribute to maintaining a closed network once the invitation is, accepted. Despite this, the benefits offered by blockchain technology may not be as distributed as public blockchains. As the network starter, you can only control what an entity can see and validate.
Businesses often use private blockchains intra-company. It allows only organization members to have access to it. This is useful only for businesses that don’t wish to share the chain with anyone outside the organization. Therefore, certain individuals can be, restricted to certain data based on their needs. Because there are fewer people in the chain, the ledger is faster and more efficient and the consensus process is easier.
Read which one should you select amongst Iconic and React Native for your next project, in our detailed blog.
Similarities between Public and Private Blockchains

Let’s look at some of the similarities between public and private blockchains before moving on to the varying differences:
Immutability: Regardless of whether they are public or private, blockchain technologies are immutable. Authenticated data (called blocks) are invulnerable to complete alterations or erasure by a single person or a large group of people.
Authentication: In both public and private blockchains, users and members are responsible for verifying and authorizing edits such as adding new transactions or activities.
Peer-to-Peer Ledger Replica: In order to avoid instances of illegal tampering, public and private blockchains both maintain and distribute real-time replicas of data or blocks across all computers or users (called nodes) on the network.
Differences Between Public and Private blockchains
Magnitude: Private blockchains are lighter and have higher transactional throughput due to the lower number of transactions they facilitate, as opposed to public blockchains, which are heavier due to the high number of transactions they facilitate continuously.
Level of Access: The process of adding and verifying data on a public blockchain is open to anyone in the world. Private blockchains, however, can only be, accessed by authorized entities.
Control: Private blockchains are, known for their centralization of network control, whereas public blockchains are, known for their decentralization of control among all users.
Security: A public blockchain is more secure due to its decentralized nature and the active participation of its users. Since very few players control private blockchain networks, there is a higher risk of hacks, breaches, and insider manipulation.
Choosing between Public and Private Blockchain
Public blockchains are more accessible to enterprises, whereas private ones are more secure. In that case, blockchain technology can still be, tamed.
Public blockchain’s value will continue to increase as its security capabilities become stronger. Private blockchain will be less necessary as a result. The private blockchain is simply too important when it comes to restricting access to a specific group of people. Ultimately, the choice is, determined by the kind of utility an organization provides.
The Power of Hybrid Blockchains

In the end, public chains and private chains have their advantages and disadvantages, so why not combine them? An alternative to a purely internal or purely global network could be one with public and private components.
Think of an ecosystem of chains or a primary chain, that is completely transparent, interoperable, and communicates with each other and with the private chains that companies can create. Despite being, built from the ground up to serve the same purpose as the public chain, these private chains are still extensions of the public chain.
Here are many advantages. Businesses can still maintain exclusive control of their own data, while the information they do release remains cryptographically verifiable – not to mention immutable, providing greater transparency than traditional enterprises ever have.
In addition, thanks to decentralization and multiple public nodes, these internal networks will remain fast and efficient, but will also benefit from the additional security provided by the larger blockchain ecosystem. In order to attack one of these private chains, the attacker would have to attack a vast network of nodes, which is a long and tedious process.
Scalability is another consideration. With multiple chains, the system can now scale more easily. The private chains themselves can scale easily due to their internal centralization, and a larger chain can scale better since it does not have to keep track of every transaction on a single ledger. Moreover, higher transaction speeds will also be, achieved in the chain’s public areas. Still, thanks to the cryptography used, the validity of any transaction can be, verified, even when the details of it are, permissioned.
Last but not least are the cost savings. In addition to improving scalability and performance, this new network will also lower fees. With only a modest upfront investment in equipment, businesses can take advantage of the robustness of this global network.
Putting Hybrid Blockchains To Work
One of the benefits of hybrid blockchains is that setting up the technology will be similar to setting up a private blockchain right now in terms of costs and complexity. The network most companies already have in place should be, able to be, adapted, and at worst, the upgrade would cost the same as any other modern server upgrade.
Once the internal system is, functioning, the private blockchain will be, linked to the public chain, which would require the installation of client software on all devices intended to connect to the network. Since most companies already have always-on systems in place, the nodes would need to run 24/7 anyway, and the energy usage should be comparable.
By using privacy bridges, Aleph Zero enables anyone to use its hybrid blockchain. Our multichain privacy framework called Liminal allows developers to keep most of their existing codebases intact and identify privacy components with our bridges then bridge to it.
In Liminal, security is, achieved through a combination of “zero-knowledge” proofs (ZK-SNARKs) and secure multiparty computation (sMPC). The combination of these two data protection tools works to eliminate each other’s weaknesses. Multi-user interactions are not possible with ZK-SNARKs. As a standalone system, sMPC is often prohibitively slow. They form the basis of Liminal, a platform that is fast, secure, and highly private.
Once a hybrid blockchain is in place, it can be, used in a variety of ways from business to entertainment to finance, among many others. An investor who holds Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple, for example, needs to use a unique application for each, and many investors have a number of cryptocurrencies to keep track of. There are some multi-chain wallets available, such as Atomic Wallet and Exodus, but supporting all of them at once is challenging.
As opposed to Ethereum’s model, where the underlying asset is, coded to act as a new asset, hybrid chains can host a variety of assets on a single network. A larger ecosystem could be, constructed with a wide range of chains that could connect to each other using para chains – individual blockchains based on individual projects that run on Polkadot – to allow information and value to be, transferred between them.
An interface that can handle all assets and act as a fast, free, and trustless exchange would be able to handle all assets natively. Using the underlying protocol, all of this will be, handled safely and trustlessly.
Additionally, using smart contracts to simplify automatic payments for everything from consumer goods to taxes would be another great use of this technology. Payment agreements should be, solidified on-chain to ensure transfers can happen regularly, or when certain conditions are, met, without human intervention. If implemented correctly, this may streamline the way businesses operate and reduce overhead.
Advantages of Hybrid BlockChain Technology
Also, the Internet of Things is, set to be, revolutionized by this technology. With the widespread use of smart devices in our daily lives, privacy concerns and data security concerns become more pressing. With more devices come more entry points for attacks, and increased access to personal data via these devices means an even greater need for security.
It is fortunate that hybrid blockchains facilitate secure data sharing between IoT devices and the wider network in such a way that only privileged parties can decrypt the data. Private chains for managing IoT systems would not be accessible on the public chain. For example, an organization may install IoT sensors around the globe to monitor a variety of metrics concerning the organization’s activities. To make all of this work, the devices would need to communicate, and a blockchain would need to manage and organize their data.
In order to keep the information secure, this could all be, handled with a private chain. It would however be easier to share information with other companies and organizations. If this private chain were part of a larger hybrid network. While this is going on, no one outside of the company would have access to any internal information. Nonetheless, it allows cryptographically verifiable information to be, communicated across the network while creating an effective barrier.
A hybrid blockchain also provides unique opportunities when it comes to Supply Chain Management. Once again, by combining public and private data, every step of the supply process can be, tracked and authenticated. And businesses can control what information other parts of the supply chain are, allowed to see. Moreover, shareholders and regulators can rest assured that reporting is, conducted with cryptographic security.
Taking this technology into the realm of entertainment, it has enormous potential in developing new forms of virtual assets for video games. In the virtual world, items do not have to be, “stuck” in the game the way. They have traditionally been due to smart contracts and NFTs. The things gamers earn, craft, or buy will now be, able to truly be their own. Which means they can be, resold on secondary markets or even transferred between different platforms.
Ares of use of Hybrid BlockChain Technology
The technology is already being, used in some games, including Axie Infinity, The Sandbox, and even virtual worlds like Decentraland. Metaverses of interoperable video game worlds are almost certain to become a reality soon. Every product could run on its own side-chain with its own assets and parameters. However, all are able to transfer information between them on the main chain, including their profiles, values, and items. Video game platforms will never be the same.
In a hybrid blockchain, businesses won’t have, to decide which blockchain is, best for them, because the strengths of both can be, integrated into their workflow. When it comes to enterprise solutions, hybrid solutions. They are likely to rise to the top in the coming years, but businesses should not wait. Leading in this arena may be what separates companies that lead from those that follow in the next decade.
To Summarize
Multiple blockchains can contain data. Whether it’s public, private, or permissible. It can include any number of unique features, from voting power to permissions to visibility. A private blockchain can be, tailored to specific data needs. With a public blockchain ledger, businesses can enforce more stringent policies.
Whether the blockchain ecosystem is public or private. Our outsourcing team of blockchain experts can help your organization fully utilize it. We can also make use of both public and private blockchain in order to create innovative solutions. Cross-chain exchanges will be, achieved with this method, and the system will be more compatible. Utilize blockchain app development to benefit your business and make the best decision.