Startups have an insecure position in the market. Unlike strong brands that have a strong reputation, loyal customers, and a great deal of trust, new companies must start from scratch. Negative reactions and customer churn can result from the slightest misstep in a new product.
Startups need to pay close attention to every detail before launching a product due to the high level of competition and the rise of new companies. This is where the role of a good UX Designer comes into play.
First impressions are shaped by design. A user will be unlikely to use a product again if they feel confused about the next steps. As a result, offering valuable features is not enough to maintain customer engagement. It’s important to maintain the software’s functionality so that users continue to interact with it.
This can be done with the help of a UI/UX designer. Software developers build software with the goal of delivering a positive user experience. As we look at UX designers’ responsibilities in a digital startup, we’ll answer the question. What does a UX designer do?
Why do you Need a UX Designer for your Project?
Designing a positive user experience is the responsibility of a UX designer. As a result, their high usability and attractive user interface contribute to brand development. UX designers are essential for any project. From beginning to end, UX designers are involved in the development process and design product interactions keeping the user in mind. UX designers provide the following benefits to your team:
Cost savings – Since the software concept is well thought out from the start, you’ll spend less time and money on reworking. Also, designers are often cheaper than programmers. As a result, it’s better to spend money on UX design and plan the user flow carefully than to correct mistakes later.
Cross-platform development – Designers of UI/UX interfaces work with multiple types of devices. As an example, they consider how everything will look on a laptop, a smartphone, and a tablet. As a result, the overall development costs are reduced because the team knows exactly what to do and avoids many errors in the process. Furthermore, responsive design makes interacting with a product across multiple platforms equally comfortable.
Timely product launch – The launch of the product is significantly sped up when a designer is on hand. Designers are able to swiftly resolve any blockers – such as the ambiguity of a certain element – by working at the pace of the rest of the team. Designers can create an interface immediately and remove the blocker if programmers are blocked due to an unfinished interface.
Systematic product promotion – A user interface and user experience designer contributes to a holistic approach to audience engagement. Those responsible for design materials create materials in one style and oversee the choices made by developers to ensure the development process goes according to plan. A UX designer develops new features based on client needs and ensures that they are harmoniously integrated into the product.
Enjoyable user experience – Interactions are designed to convey the product’s central message. As part of the creation process, they select images, design product styles, and develop user paths. UX designers are not concerned with creating pretty pictures but rather conveying the app’s concept through an appropriate interface and a positive user experience.
Read about the skills a Good UX Designer should possess.
UI/UX Designer Role Description
Interface development can be described as what UI/UX designers do.
User interfaces (UIs) control the aesthetic and visual aspects of software, while user experiences (UXs) control functionality and navigation. It is most often one person who designs both the UI and the UX even though they are two different aspects of an application. By interacting with the product, this person creates a positive impression. Their primary responsibility is to design an intuitive user interface that helps users achieve their desired goals with the least amount of effort.
Researchers, analysts, data collectors, wireframers, and prototypers make up the daily routine of UI/UX designers. They require a deep understanding of processes and proactive analytical thinking, duties that overlap with those of business analysts and marketers.
By the same token, UI/UX design can be a creative occupation that pushes people to think outside the box and search for non-standard solutions. From the moment an app launches to the moment it is closed, a UI/UX designer ensures that users have a clear path to follow. As you can see below, UI/UX designers are concerned with the user experience and the user interface.
In terms of the UX:
- Achieves product goals by selecting appropriate UX tools
- Facilitates the use of the product by the target audience
- Evaluates whether the product is meeting the customer’s expectations
- Based on results, edits/changes
In terms of the UI:
- Designs each page and screen in terms of its concept
- Design each screen and page with visual components
- Ensures graphical elements are consistent with the corporate identity
- Provides a design that can be adapted to different screen resolutions
What does a UI/UX Designer do?

As a part of the product development team, the UI/UX designer creates user interfaces and user experiences. Throughout the entire product lifecycle, including planning, development, testing, release, and maintenance, they are directly involved. Designers also act as mediators between developers and users, in addition to performing basic functions.
By applying UI/UX best practices and techniques, they work closely with developers to implement user wishes. Designers are always guided by business concerns at the same time. A UI/UX designer takes into account the potential benefits of a certain feature to the company, as well as how it will fit with the idea of the entire product.
A UX designer’s main job is to ensure that the user’s journey proceeds logically. Creating a tangible product begins with a sketch. In this process, designers perform many different tasks. Here are the tasks and responsibilities of a UX designer in a software development project

Product research
Market, user, and competitor research are integral parts of product research. From here, the designer begins their quest to create a product that is valuable to stakeholders and customers alike. During this stage, the product is viewed from the point of view of the users.
Data collection and information systematization make up product research. The designer decides who needs what at the start of the project.
By conducting surveys, collecting data, browsing literature, evaluating data, and considering analytics, etc., they can do this. Design is an iterative process, and studies can be revisited as the project progresses.
Methods of UX research can be categorized into quantitative and qualitative categories:
Quantitative research produces numerical results. Examples include: How many times did people click on this link? What percentage of users could locate the call to action? A quantitative indicator helps designers understand statistical probabilities and what is occurring on a website or in an application.
Qualitative research examines users’ intentions. Understanding people’s motivations and why they act and how they do helps designers develop their products. Qualitative research is typically conducted through interviews. In this step, a UX designer looks for solutions to questions such as Why aren’t people seeing the call to action? How does the page look to visitors?
Persona development
In the product research stage, creating user personas is one of the main artifacts designers receive. The designer is able to determine who the program is meant for and what problems it aims to resolve through interviews, user analysis, and immersion in the product environment.
In their understanding, a user persona represents a real user. This section describes key demographic information about this target audience, such as age, occupation, and marital status.
Personas assist UX/UI designers in better understanding the product’s target audience and identifying critical problems, needs, and pain points. This ultimately leads to an improved user experience, increasing the product’s value and appeal to prospective and existing customers. Informed decisions are made with well-designated user personas.
Therefore, UX designers do what their clients expect and receive higher engagements as a result. User experience designers, for example, know what features users find useful, what logos they like best, and what text they understand most quickly.
One project typically involves several user groups and is not limited to one persona. Different people have different ethnic backgrounds, socioeconomic levels, interests, and daily activities. Moreover, when they interact with your app, they may seek different things.
Thus, it is crucial to identify and meet the needs of each type of persona.
Read About .NET 6, in our blog.
Information architecture setup
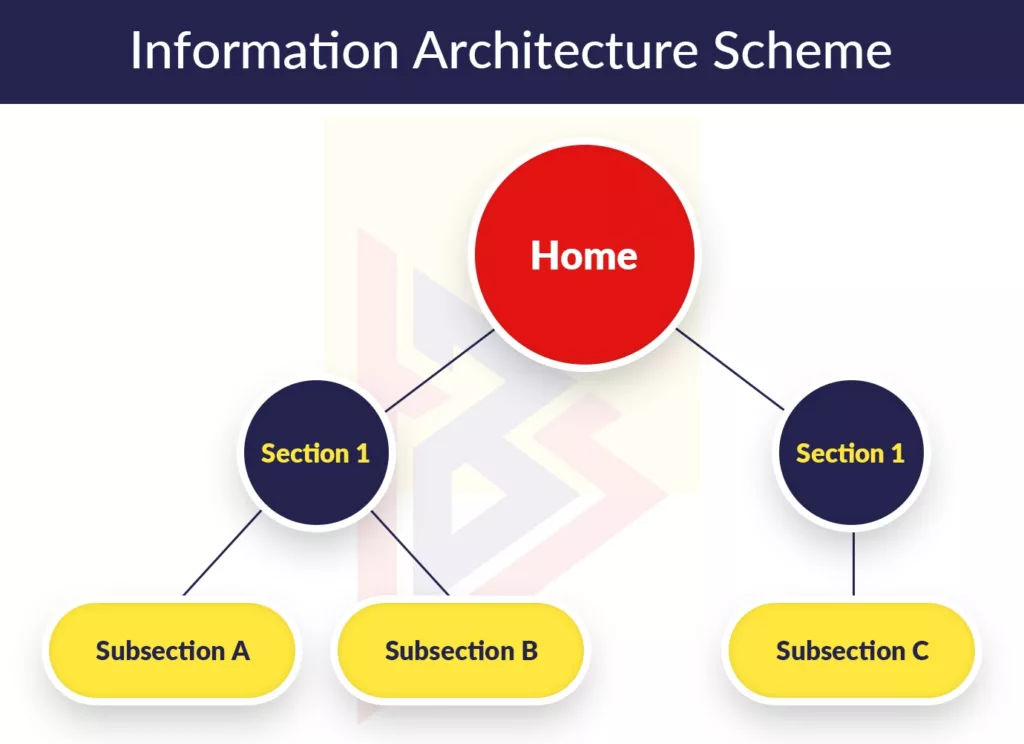
Developing personas is followed by the creation of information architecture (IA) for the product. The aim of this is to organize content so that users feel confident when navigating the app or website. In the development of any product, defining the information architecture lays the foundation for building features and creating the UI.
During the IA stage, the user flow and sitemap/app map are created. Product wireframes are the major output. These graphics depict the user interface in a low-detailed manner and provide the main groups of content (what will be on the screen) and information structure (where it will be placed on the screen).
Here’s what a UX designer does to create the information architecture:
- User research – Communication and analytics are used to conduct user research that produces detailed user personas.
- Content sorting – Among these things are headings, subheadings, media, documents, links, etc. Designers have the task of separating content elements into screens, sections, and topics. These elements should then be added to the content template.
- Navigation building – No matter where they appear in your app, users must know how to find the information they are looking for. To do this, the UX designer creates a hierarchical structure, designs patterns, and draws complex navigation maps.
Wireframing
Now that we have the software structure in place, we can begin developing screens. Wireframing is essentially sketching every page for a UX designer to create. Wireframes are primarily used for demonstrating the overall functionality of a product. A wireframe shows how the users will see the interface elements on the most important screens, including navigation, data visualization, and basic actions.
In addition to the architecture and hierarchy of the content that will be displayed, wireframes help to define the product’s fundamental structure. For example:
- The page consists of what elements?
- What is the purpose of their presence?
- Do they have a location?
- What is their purpose?
Designers present wireframes at scheduled demo meetings to ensure they’re on the right track. Those who view wireframes are more focused on functionality rather than aesthetics. A lack of visual design allows people to make quick changes without being distracted by unnecessary details. By prioritizing tasks through the workflow, designers are more likely to be productive throughout the design process
Read about the best ASP.NET Tools for development.
Prototyping
Based on the wireframes, we will create a clickable prototype. Even though it’s grayscale, a clickable prototype is interactive. A dynamic wireframe lets users navigate between screens, click buttons, scroll pages, and perform other actions that aren’t possible with a static one.
Prototyping should be less detailed than using the final product. Some elements may be missing, and colors may be lacking. However, it provides insight into the product’s functionality and the way users interact with it.
Prototypes are presented to stakeholders, developers, and end users. They then provide feedback to designers on what should be changed.
UI design
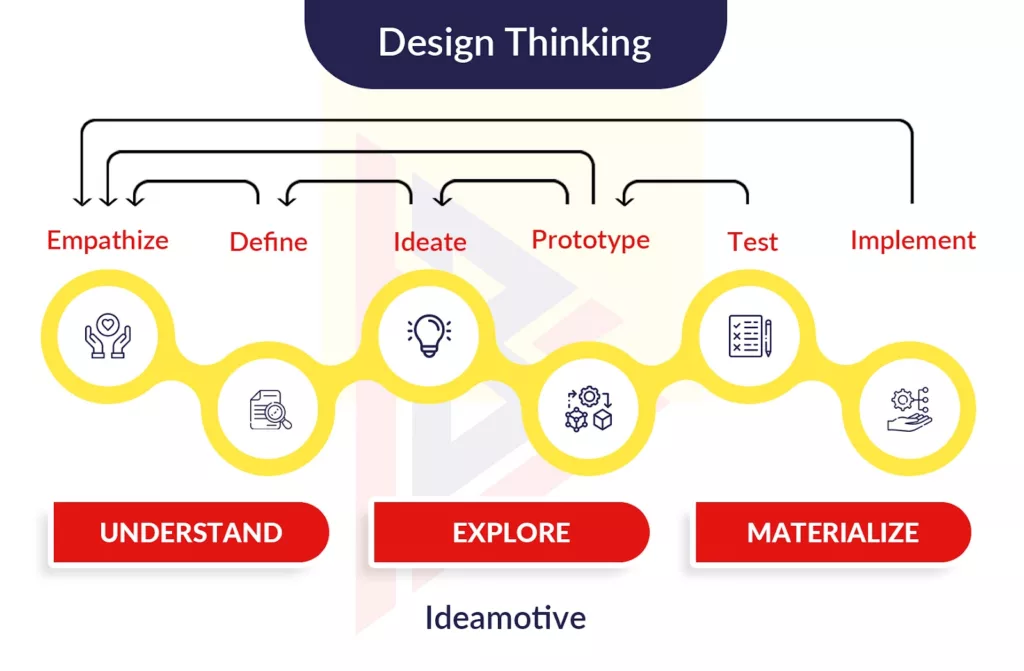
Designing a product’s visual identity is one of the biggest challenges. If UI/UX designers choose the right style for the product, regardless of whether it is trendy, boring, futuristic, or anything else, they can believe their work is of high quality.
Differentiating your product from your competitors is also crucial. In the event that your product looks similar to others, understanding the brand and offering the right colors may not be enough. A UI/UX designer needs to devise innovative solutions that fit the app’s idea and make it stand out.
UI/UX designers visually arrange each screen’s contents in the most convenient way at this step. Additionally, they design stylized and responsive screens with all states and scenarios previously outlined in wireframes.
When designing an interactive element, a designer assesses whether it appears at the right time, if it is easy to scan, and if the information is easy to absorb. UX/UI designers also take care of elements’ states and behaviors.
Our designers follow the Atomic Design methodology during the UI design stage at TechnoBrains. This tool helps them plan out every component in detail and create interfaces from small to large. Future mockups can be created by using design components. This method can help the designer maintain consistency over the course of the project, quickly change interface elements, and scale them as needed.
UI designers create a UI kit and style guide for developers in the final stage. As a result of adhering to them, the team stays on track throughout the project and speeds up development.
Usability testing
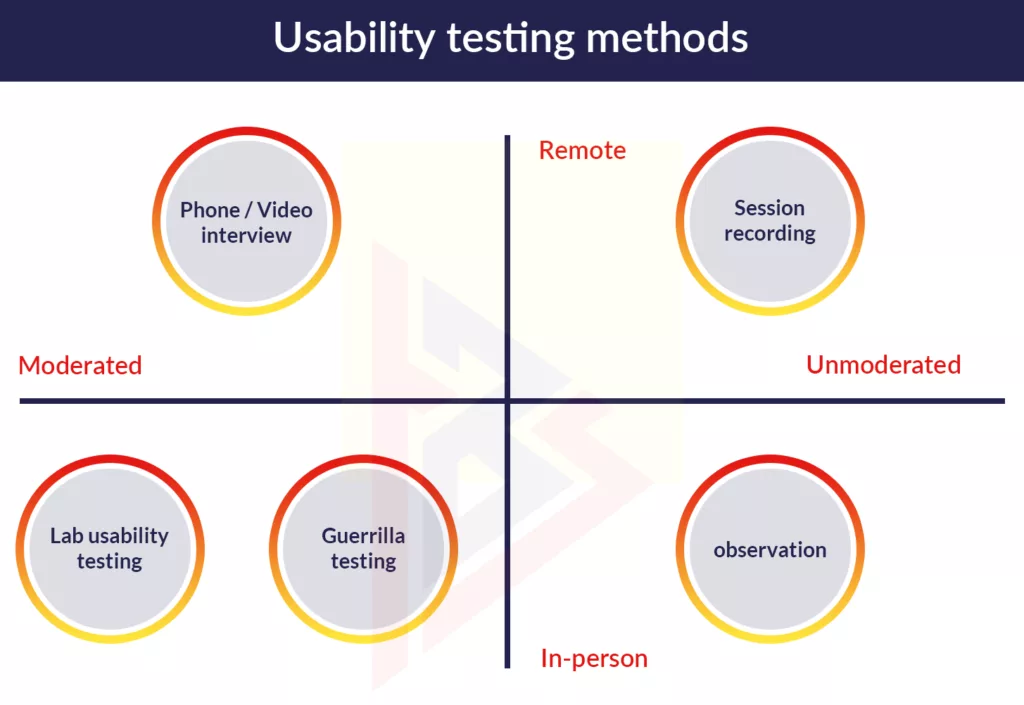
The team uses usability testing to ensure that its software design is effective. At first, the team members perform the testing themselves. Real users, however, who use the product for some time and share their impressions, provide the most relevant results. Data is collected and analyzed as part of usability testing.
Usability testing can be divided into:
- Unmoderated and moderated
- Both in-person and remote
- Comparative, exploratory, and assessing
Depending on the size and nature of the project, the designer selects the most appropriate method. In addition, a designer cannot alter the progress of testing during implementation.
UI/UX designer hard and soft skills
A quality product needs to keep pace with users’ needs and business goals, which is where the UI/UX designer comes in. The best UI/UX designers use the latest technologies, understand how to use advanced tools, and have a creative mind that offers non-standard solutions.
UI/UX designers need to have both hard and soft skills, in addition to hands-on experience when hired. A good designer should have the following profile. When selecting candidates for your project, you can refer to it as a guideline.
Conclusion
A UI/UX designer is responsible for solving both functional and aesthetic problems. User journeys and experiences are shaped by the former; visual concepts follow the brand’s intentions. An appealing design already makes a lot of difference.
Understanding clients’ and users’ needs is the key to a successful launch. Professional designers translate clients’ ideas into high-quality products. The designers’ contributions are crucial to the success of any project.
How can TechnoBrains Help You?
Would you like to improve your UX experience or would you like help with UX design services? TechnoBrains‘ user experience consultants and designers work with you to understand your customers’ behaviors, their requirements, and their online needs.
As one of the leading providers of UX design services, TechnoBrains’ UX design experts can help your organization with user experience design and navigating the digital landscape.